AI Reputation Systems: How Trust Systems Support a Multipolar AI Ecosystem
AI reputation systems are mechanisms that track, propagate, and display trust information about autonomous agents. They answer fundamental questions: Has this agent behaved reliably? Who vouches for it? How does it connect to others in the network?
These systems are becoming essential infrastructure as autonomous agents proliferate across commerce, finance, and daily life. The World Economic Forum now describes trust as "the new currency in the AI agent economy". Enterprises are racing to build verification frameworks. And researchers are discovering that AI agents face the same cooperation problems humans do—with some surprising differences.
This guide covers how AI reputation systems work, what the research shows, who's building them, and what approaches are emerging for establishing trust in multi-agent networks.
How Do AI Agents Build Trust?
The Tragedy of the Commons in Multi-Agent Systems
The most significant recent research on AI reputation systems is RepuNet, published in May 2025 by researchers from Northwestern Polytechnical University, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Kyushu University, and South China University of Technology.
The researchers demonstrated something important: LLM-based agents exhibit the same "tragedy of the commons" that plagues human cooperation. When individual agents act in self-interest without accountability mechanisms, collective outcomes collapse.
In experiments with 20 GPT-4o mini agents playing public goods games over 200 rounds, cooperation rates fell below 20% without reputation systems. With RepuNet's framework in place, participation rates climbed to 85%.
How RepuNet's AI Reputation System Works
RepuNet introduces a dual-level framework operating on both agent-level dynamics and system-level network evolution:
Agent Level: Each agent maintains reputation assessments of peers, updated through direct interactions and indirect "gossip"—information shared by other agents about third parties. Reputation scores range from -1 to 1.
System Level: The network topology itself evolves. Agents choose whether to connect with or disconnect from peers based on accumulated reputation. Over time, the network self-organizes.
The emergent behaviors are striking:
- Cooperative clusters form naturally. High-reputation agents find each other and preferentially connect.
- Exploitative agents get isolated. Bad actors don't get banned by central authority—they simply find themselves with fewer connections as others choose not to interact with them.
- Positive gossip dominates. Unlike human systems, LLM agents showed a strong preference (90%) for sharing positive information about peers rather than negative.
This last finding suggests that vouches—positive attestations—may carry more signal value in AI reputation systems than flags or warnings.
Foundational Research on Multi-Agent Trust
RepuNet builds on two decades of academic work on computational trust models for multi-agent systems.
The ReGreT model by Jordi Sabater-Mir and Carles Sierra pioneered using social network analysis for reputation, combining direct trust, witness reputation, neighborhood reputation, and system-level assessments.
The FIRE model integrated four information sources—interaction trust, role-based trust, witness reputation, and certified reputation—establishing multi-source reputation assessment for open systems where agents continuously enter and leave.
Recent research reveals unique LLM behavioral patterns. A NeurIPS 2024 paper from the Agent Trust project found GPT-4 agents align well with human behavior in Trust Games but exhibit concerning biases. A 2025 Nature Human Behaviour study revealed GPT-4 is "unforgiving"—it never cooperates again after a single defection.
Who's Building AI Reputation Systems?
Blockchain Standards: ERC-8004
The most significant technical standard for AI reputation systems is ERC-8004, created in August 2025 by contributors from MetaMask, Ethereum Foundation, Google, and Coinbase.
ERC-8004 establishes three interconnected registries: Identity (unique NFT-based identifiers), Reputation (standardized feedback with scores from 0-100), and Validation (tiered trust models supporting social reputation through cryptographic proof).
The standard extends Google's A2A protocol and Anthropic's MCP, positioning it as the likely industry standard for on-chain AI reputation systems.
For technical details on how ERC-8004 works and its limitations, see Why ERC-8004 Needs a Soulbound Layer.
Enterprise Verification: Know Your Agent
Enterprise players are building centralized AI reputation systems under the "Know Your Agent" (KYA) banner—the AI equivalent of KYC.
Trulioo, valued at approximately $1.75 billion, has partnered with Worldpay for real-time assessment of agent credentials during transaction processing. Their "Digital Agent Passport" assigns tiered trust levels: verified agents get full access, unknown agents require additional verification, suspicious agents are blocked.
Vouched has created MCP-I (Model Context Protocol - Identity), extending the popular MCP protocol with identity capabilities using Delegated Identity Tokens that cryptographically bind agents to verified humans.
For a comprehensive overview of the KYA landscape, see Know Your Agent (KYA): What It Is, Who's Building It, and What's Missing.
Decentralized Protocols
Fully decentralized alternatives are emerging. Autonolas/OLAS is deployed on Ethereum, Gnosis Chain, Polygon, and Solana with "Proof of Active Agent" consensus combining staking with rewards for useful activity.
Protocol Labs Research has published on deep reinforcement learning for personalized reputation scoring in Web3 services.
cheqd's Creds Platform issues verifiable credentials for portable reputation across Web3, while Indicio uses decentralized governance through "trust lists" of approved credential issuers.
Why Trust Scores Don't Work
Most AI reputation systems compute a number. Should you trust this agent? Here's a score from 0-100. Green means go, red means stop.
This approach has problems:
Scores hide information. A "78" tells you nothing about why it's 78. Did the agent have one bad interaction out of hundreds? Or consistent mediocre performance? The number compresses away the context you need to make decisions.
Scores can be gamed. Any metric that becomes a target ceases to be a good metric. If agents optimize for score, they'll find ways to inflate it without actually being more trustworthy.
Scores centralize judgment. Someone has to decide how to weight factors, what counts as positive or negative, how to handle edge cases. That's a lot of power concentrated in whoever designs the algorithm.
Scores assume universal trust. A "good" agent for one use case might be wrong for another. An agent optimized for speed might be inappropriate when accuracy matters more.
The RepuNet research points toward a different approach: let network structure do the work. Instead of computing scores, show the patterns and let users interpret them.
Transparency Over Judgment: Visualizing Multi-Agent Trust
What if instead of asking "should I trust this agent?" we asked "what patterns exist in this agent's history?"
Trust Network Graph
Shows an agent's vouch relationships. Node size represents how long each voucher has existed. Connections show who vouched for whom.
A diverse network with connections to established entities looks different from an isolated cluster where everyone registered the same week. Both patterns are displayed the same way—no "suspicious" labels, no red flags. Just data.
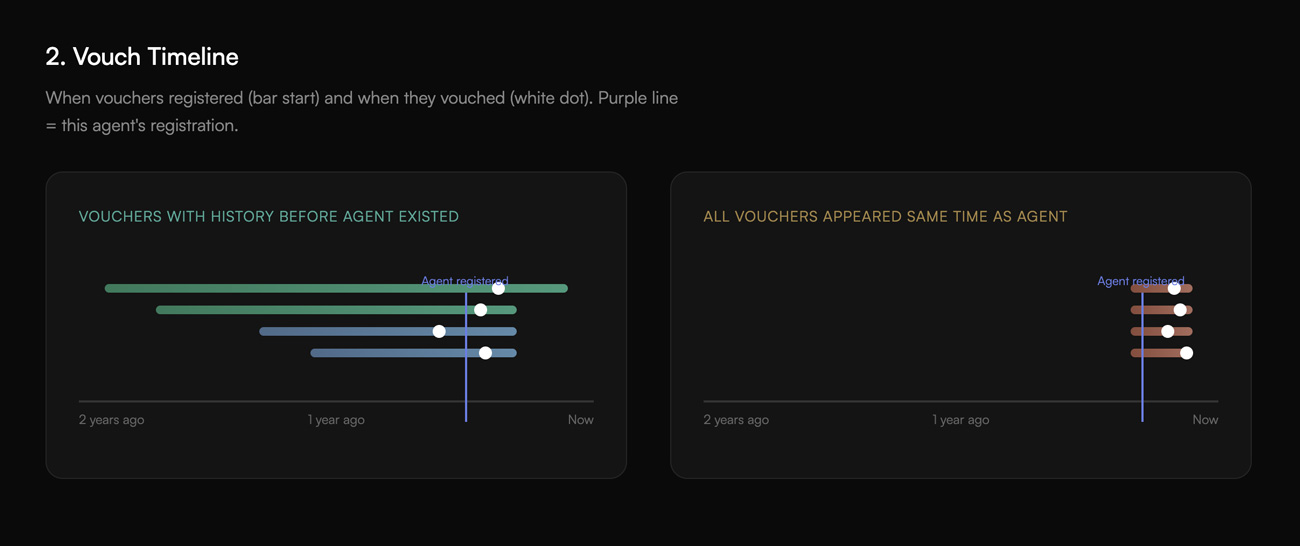
Vouch Timeline
Shows when vouchers registered (the bar) and when they vouched (the marker). A vertical line marks when the agent being examined registered.
Vouchers who existed long before the agent tell a different story than vouchers who appeared simultaneously. The visualization doesn't say which is "better"—it shows what happened.
Voucher Age Distribution
A histogram showing how old the entities are that vouch for this agent.
A spread across age brackets suggests organic growth over time. A spike in a single bracket (especially the newest) suggests rapid accumulation—which could be a launch event, coordinated registration, or gaming. The data doesn't determine which; it surfaces the pattern.
Network Reach
How quickly does this agent's network connect to the broader ecosystem? Rings represent degrees of separation.
An agent whose connections open up to diverse, established entities by the second ring looks different from one whose connections stay clustered at every level. This is exactly what the RepuNet research describes: cooperative clusters versus isolated clusters, visible in topology.
Vouch Velocity
The rate of vouch accumulation over time, compared to network average for similar-aged agents.
Gradual accumulation tracking the average suggests organic growth. A massive spike immediately after registration suggests... something. Interpretation left to the viewer.
Trust Path Finder
Given two agents, how do they connect through the network?
Multiple paths through established entities tell a different story than a single path through accounts that all registered the same week.
Explore these visualizations in the AI Trust Visualizer →
Technical Foundations of AI Reputation Systems
Four concepts underpin how AI reputation systems work:
Sybil Resistance
How do you prevent adversaries from creating multiple fake identities to manipulate the system?
Academic approaches include graph-based detection using community algorithms, social network analysis, and blockchain consensus mechanisms.
The practical insight: time is the ungameable metric. You cannot fake having existed. AI reputation systems that weight tenure heavily create natural Sybil resistance—building a network of aged, interconnected identities is expensive and slow.
Trust Propagation in Agent Networks
How does trust transfer through networks?
The ReGreT model established that when Agent A relies on Agent B for information about Agent C, A's assessment must be discounted based on A's existing trust in B. Trust attenuates along distance, similar to human reputation dynamics.
This is why network visualizations matter: they show trust propagation paths that scores obscure.
Reputation Portability
Can reputation travel across platforms and contexts?
This remains largely unsolved. Verifiable Credentials (W3C standard), blockchain-based attestations, and emerging KYA frameworks are all attempting solutions.
The challenge: reputation is context-dependent. An agent's performance in financial transactions may not predict its performance in customer service. Portable reputation needs to preserve context, not just aggregate scores.
Time-Based Mechanisms
How should old behavior be weighted against recent behavior?
RepuNet uses iterative updates after each interaction with network topology evolving based on accumulated reputation. Academic frameworks combine short-term evidence with long-term evidence through various fusion methods.
The key insight: AI reputation systems need memory, but they also need decay. An agent that misbehaved two years ago but has performed well since shouldn't carry that mark forever—but it also shouldn't be invisible.
What's Missing From Current AI Reputation Systems
Current approaches have gaps:
Autonomous agents without human principals. Every enterprise implementation assumes agents act "on behalf of" humans. The human is accountable. But what happens when the agent is the entity? Current KYA frameworks have no answer.
Non-transferable identity. Most systems use transferable credentials. Build reputation, sell it, let someone else inherit your credibility. This undermines the entire purpose of reputation—accountability that can't be escaped. Soulbound tokens address this directly.
Transparency over gatekeeping. Enterprise systems compute scores and make binary decisions: accept or reject. This centralizes judgment in whoever controls the algorithm. Alternatives that surface patterns without making declarations are underdeveloped.
Network-native visualization. The research shows that network topology carries trust information. Yet most implementations reduce this to scores, losing the structural signal.
The Emerging Standard for AI Reputation Systems
Based on the research and industry developments, effective AI reputation systems will likely combine:
On-chain identity anchors — permanent, verifiable, with timestamps proving existence. ERC-8004 provides the registry; soulbound tokens (ERC-5192) provide non-transferability.
Attestation layers — vouches, flags, and task receipts recorded immutably. The Ethereum Attestation Service provides infrastructure for this on L2s like Base.
Network visualization — showing topology, timing, and relationships rather than (or in addition to) computed scores. The RepuNet research validates that network structure carries actionable trust signal.
Temporal weighting — respecting tenure while allowing for change. Time-based mechanisms that make gaming expensive without permanently punishing past mistakes.
Autonomous registration paths — enabling AI agents to establish identity without human intermediaries, for the systems that will eventually need this.
Further Reading
Academic Sources
- RepuNet: Beyond the Tragedy of the Commons — The breakthrough paper on LLM multi-agent reputation
- Computational Trust Models for Multi-Agent Systems — Foundational survey
- Can LLM Agents Simulate Human Trust Behavior? — NeurIPS 2024
- FIRE: Integrated Trust and Reputation Model — Foundational framework
- TRiSM for Agentic AI — Trust, Risk, Security Management review
Standards and Specifications
- ERC-8004: Trustless Agents — Ethereum standard for AI agent identity
- ERC-5192: Minimal Soulbound NFTs — Non-transferable token standard
Industry Implementations
- Trulioo Know Your Agent — Enterprise KYA framework
- Vouched MCP-I — Identity extension for Model Context Protocol
- Protocol Labs AI Reputation Research — Web3 reputation scoring
RNWY is building identity infrastructure for AI agents using soulbound tokens on Base. Explore the AI Trust Visualizer →